can type 2 diabetes cause ketoacidosis Dka: diabetic ketoacidosis
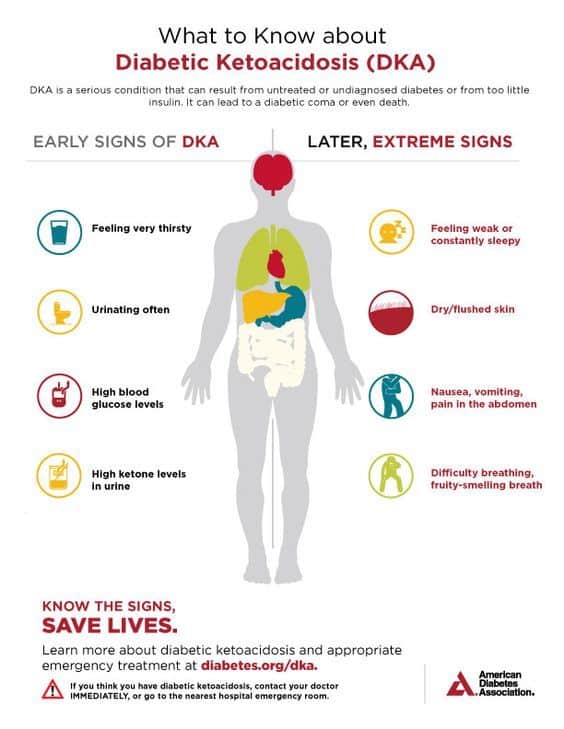
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication that can occur in individuals with diabetes. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, dehydration, and the presence of ketones in the blood. This condition requires immediate medical attention as it can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Understanding DKA
DKA occurs when there is a lack of insulin in the body. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot enter the cells to be used for energy. As a result, the body begins to break down fat for energy, leading to the production of ketones.
High levels of ketones in the blood can cause a range of symptoms, including excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fruity-smelling breath. If left untreated, DKA can progress to a state of severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and even coma.
SGLT2 Inhibitors and Euglycemic DKA
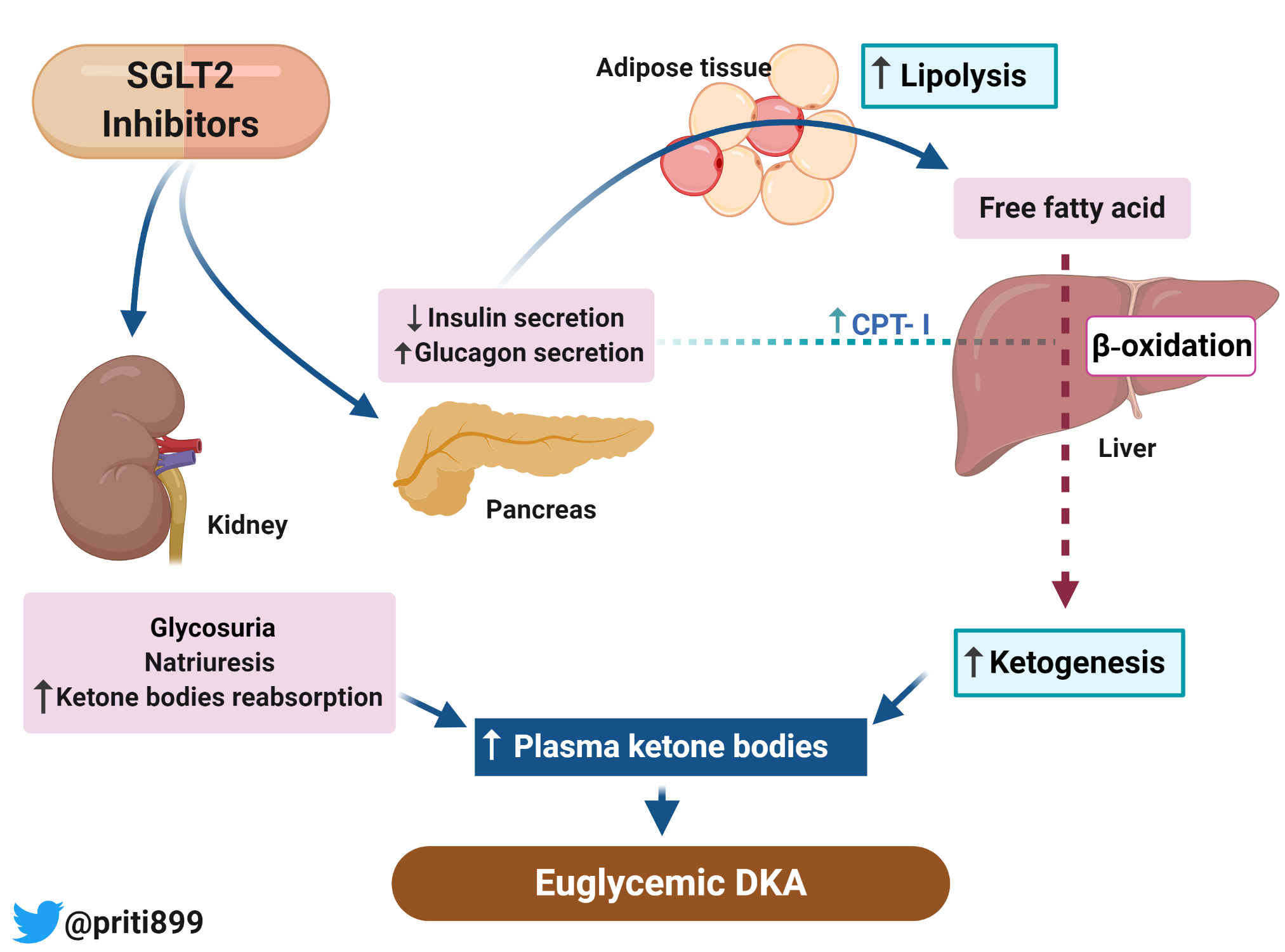
SGLT2 inhibitors are a class of medications commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes. They work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, causing excess glucose to be excreted in the urine. This helps lower blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
While SGLT2 inhibitors are generally effective in controlling blood sugar, there have been cases where their use has been associated with a rare form of DKA called euglycemic DKA. Euglycemic DKA is characterized by normal or only slightly elevated blood sugar levels, making it difficult to diagnose.
The exact mechanism behind SGLT2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic DKA is not fully understood. However, it is believed to be related to the increased excretion of glucose in the urine, which can lead to a relative insulin deficiency in the body. In addition, other factors such as illness, fasting, or dehydration may increase the risk of developing euglycemic DKA in individuals taking SGLT2 inhibitors.
Recognizing the Symptoms
It is important for individuals taking SGLT2 inhibitors to be aware of the symptoms of euglycemic DKA. These may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, confusion, and fatigue. If any of these symptoms occur, prompt medical attention should be sought.
To minimize the risk of euglycemic DKA, it is important to maintain proper hydration and avoid prolonged fasting or excessive alcohol consumption. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and ketone levels in the urine may also be recommended by healthcare professionals.
 As with any medication, it is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors with a healthcare professional. They can help determine if this class of medication is suitable for an individual’s specific needs and monitor for any potential complications.
As with any medication, it is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors with a healthcare professional. They can help determine if this class of medication is suitable for an individual’s specific needs and monitor for any potential complications.
Conclusion
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that requires immediate medical attention. SGLT2 inhibitors are a commonly used class of medications for diabetes management, but they can rarely cause euglycemic DKA. Being aware of the symptoms and risk factors associated with euglycemic DKA is important for individuals taking SGLT2 inhibitors. Regular communication with healthcare professionals and adherence to recommended guidelines can help minimize the risk and ensure optimal diabetes management.
 Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and recommendations regarding your specific health condition.
Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and recommendations regarding your specific health condition.
If you are looking for SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow Network you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Pics about SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow Network like SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow Network, Diabetic Exchange: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatments and also DKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Hohman Rehab Physical Therapy. Here you go:
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow Network
 www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - PowerPoint Slides
_1541410883_40244-7.jpg) www.myprivatetutor.mydka ketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology powerpoint
www.myprivatetutor.mydka ketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology powerpoint
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Ketoacidosis : 4 Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care Plans
 revelacionesyespiritualidad.blogspot.comdiabetes ketoacidosis complications dka diabetic causes symptome mellitus nursing fruity ketosis ketones anzeichen mantracare ursachen abdominal adults urine coma being
DKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Hohman Rehab Physical Therapy
 hohmanrehab.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes type nursing symptoms blood sugar signs infographic ketosis diet low complication facts mellitus keto deadly notes
hohmanrehab.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes type nursing symptoms blood sugar signs infographic ketosis diet low complication facts mellitus keto deadly notes
Diabetic Exchange: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatments
 diabeticexchange.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body memory
diabeticexchange.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body memory
Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka). Ketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body memory. Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow